Mold and fungus are not the same; mold is a type of fungus. Fungi is a kingdom of organisms that includes molds, yeasts, and mushrooms. Mold refers specifically to multicellular, filamentous fungi that reproduce by spores and thrive in moist conditions.
Understanding Mold and Fungus: Definitions and Differences
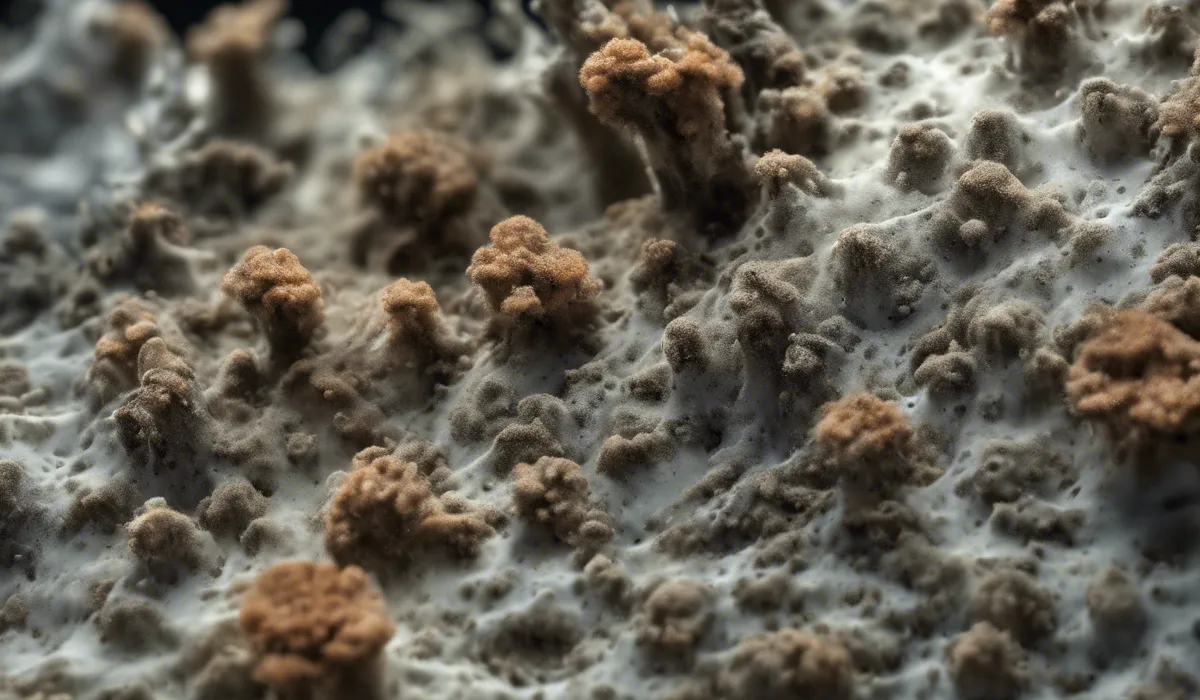

Define Mold
Mold is a type of fungus that we often see in damp places. These tiny life forms grow into clusters that look like fuzzy spots.
They come in many colors like black, white, orange, green, or purple. Molds are made up of lots of small threads called hyphae.
They spread by creating tiny seeds called spores, which float through the air to find new places to grow.
Define Fungus
Fungus is a big group of living things that are not plants, animals, or bacteria. This group includes molds, as well as mushrooms and yeasts.
Fungi can look very different from each other. Some are big like mushrooms, while others are too small to see without a microscope.
They get their food by breaking down dead things or by taking nutrients from other living things.
Explain the Relationship Between Mold and Fungus
Mold is part of the fungus family. This means all molds are fungi, but not all fungi are molds.
For example, a mushroom is not a mold, but it is a fungus. Molds share some common features with other fungi, like having cell walls and living off other things, but they also have their own special traits.
Highlight the Differences in Characteristics
While molds and other fungi can seem similar, they have different ways of living and looking.
Molds spread by spores and grow in thread-like patterns, which other fungi might not do. Molds usually need damp areas to grow, while some other fungi can grow in dry or even harsh places.
Discuss the Variety Within the Fungal Kingdom
The fungal kingdom is full of different shapes, sizes, and colors of life. Some fungi help plants grow by connecting to their roots, while others can make food go bad.
Some even glow in the dark! There are tens of thousands of fungal species, showing just how diverse this kingdom is.
Ecological Roles and Health Implications

Explain the Ecological Role of Mold
Mold has an important job in nature. It helps to break down dead plants and animals, turning them into soil.
This way, nutrients get back into the ground, helping new plants to grow. Without mold, we would have lots of leaves, wood, and other dead stuff piling up with no way to recycle them.
Describe the Ecological Role of Fungi
Fungi are like nature’s cleanup crew. They break down things that are no longer alive and make the soil richer.
Some fungi even work with living plants, giving them water and nutrients in exchange for food. This teamwork helps forests and gardens to be healthy and grow.
Discuss the Beneficial Aspects of Mold and Fungi
Mold and fungi are not just about decay. They can also be very helpful. For example, some molds make medicines that can fight off bad germs.
Fungi can also be used to make tasty foods like bread, cheese, and mushrooms. Plus, scientists are studying them to find new ways they can help us.
Address the Health Implications of Mold Exposure
Even though mold can be helpful, it can also make us sick if we breathe in too many of their spores.
This can cause problems like coughing, sneezing, and itchy eyes, especially for people who already have allergies or asthma. Some molds can produce toxins that are even more harmful, so it’s important to keep them out of our homes.
Explore the Health Effects of Other Fungi
Other fungi can affect our health too. Some can cause infections, especially in people who don’t have strong immune systems.
But just like mold, many fungi are safe and can be part of healthy food. It’s all about knowing which ones are good and which ones to avoid.
Identification and Management in Human Environments
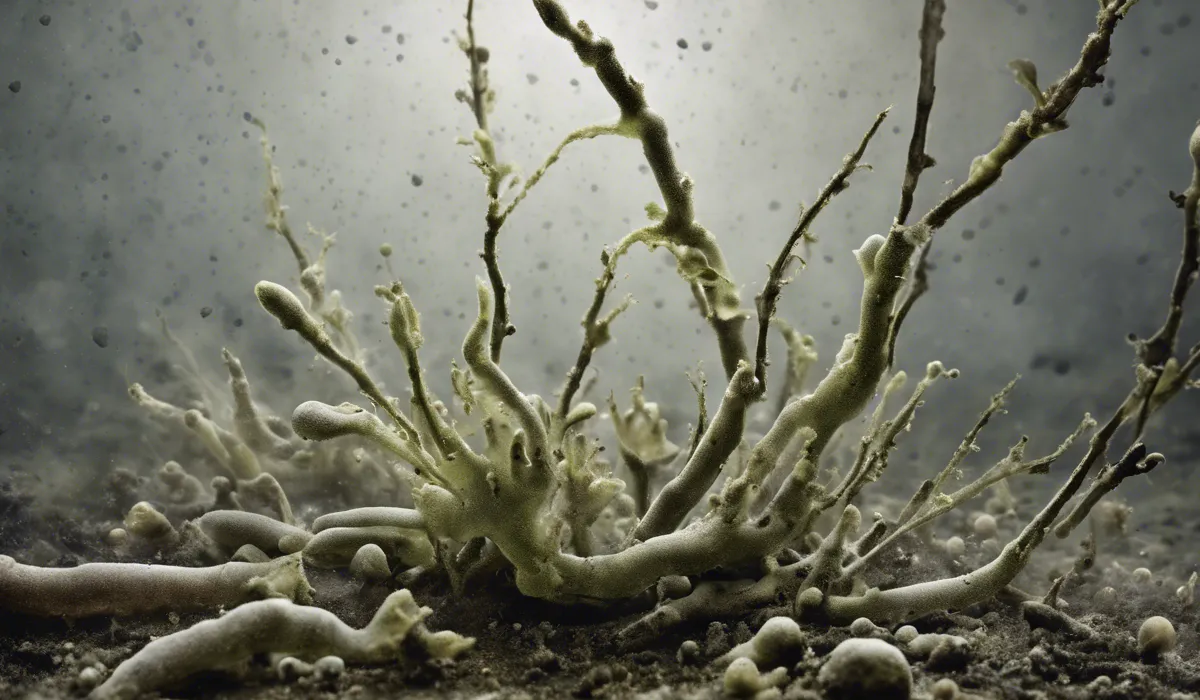
Tips for Identifying Mold vs. Other Fungi
To tell mold apart from other fungi, look for patches or spots that seem to spread out in a flat way across a surface.
Mold usually shows up where it’s been wet for a while. Other fungi like mushrooms can be identified by their unique shapes and structures that rise above the ground or the surface they’re on.
Discuss the Common Habitats of Mold in Human Environments
Mold loves damp places in our homes like bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. It can hide under carpets, inside walls, or in places where water has leaked.
Keeping these areas dry and clean can help stop mold from moving in and making itself at home.
Explain the Significance of Managing Mold and Fungi in Homes and Workplaces
It’s important to keep an eye on mold and fungi because they can harm our health and damage our homes or workplaces.
If we let them grow, they can spread and become harder to get rid of. Taking care of leaks, dampness, and humidity can stop them from becoming a problem.
Provide Strategies for Preventing Mold Growth
To stop mold from growing, make sure your home stays dry. Fix any leaks right away, use fans to move air around, and use a dehumidifier if it’s too humid.
Clean up any spills or floods quickly, and keep your home clean to make it less welcoming for mold.
Offer Guidelines for Safely Removing Mold and Mitigating Fungus-Related Issues
If you find mold, it’s important to clean it up carefully. For small areas, you can use soap and water or a cleaning product made for mold.
Always wear gloves and a mask to protect yourself. If there’s a lot of mold or if it keeps coming back, you might need to get help from people who know how to handle it safely.
FAQs About Mold and Fungus
Is mold the same as fungus?
Mold is not the same as fungus; it is a specific type of fungus characterized by multicellular filaments and spore reproduction.
Are all fungi molds?
No, not all fungi are molds. The fungi kingdom includes a wide variety of organisms such as yeasts, mushrooms, and molds.
What distinguishes mold from other fungi?
Mold is distinguished from other fungi by its filamentous structure and its ability to reproduce through spores, typically thriving in moist conditions.
Can yeast be classified as mold?
No, yeast is not classified as mold. Yeast is a unicellular fungus that typically reproduces by budding, while mold is multicellular and reproduces by spore formation.
Do mushrooms fall under the category of mold?
No, mushrooms are not categorized as mold. Mushrooms are a form of fungi known for their fruiting bodies, which are distinct from the filamentous structure of molds.
Final Thoughts
Mold and fungus are distinct entities within the same kingdom, Fungi. Molds are a subset of fungi, characterized by their multicellular filamentous structure and spore-based reproduction, typically flourishing in damp environments.
While they are related, not all fungi are molds, as this kingdom also encompasses yeasts and mushrooms.
