Mold poisoning, also known as mycotoxicosis, is not contagious. It results from exposure to mold toxins, not from person-to-person transmission. Each individual’s reaction to mold exposure is unique and depends on numerous factors, including the duration and intensity of exposure.
Understanding Mold Poisoning
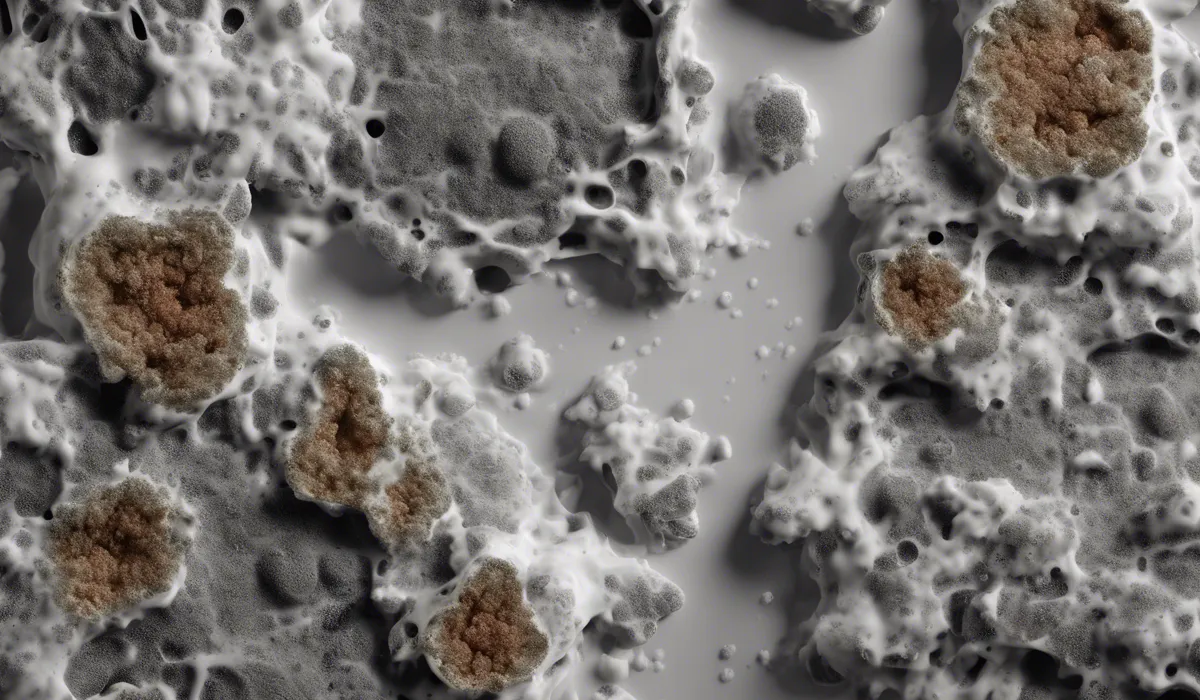
What Is Mold Poisoning?
Mold poisoning, often referred to as mycotoxicosis, occurs when an individual inhales or ingests mycotoxins, the toxic substances produced by certain types of molds. These toxins can lead to various adverse health effects depending on the level of exposure and the individual’s sensitivity.
Common Culprits: Toxic Molds
Among the various mold species, Black mold, scientifically known as Stachybotrys chartarum, and molds from the Aspergillus genus are notorious for their potential to cause health problems.
These molds thrive in damp environments and can release spores into the air, which carry the harmful mycotoxins.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of mold exposure can range from mild allergic reactions, such as sneezing and itchy eyes, to more severe conditions like respiratory issues, headaches, and even memory loss.
It is vital to recognize these symptoms early to address mold exposure promptly.
How Mold Affects the Body?
When mold spores are inhaled, they can irritate the airways, leading to respiratory symptoms. Mycotoxins can also suppress the immune system and cause inflammation throughout the body.
This can result in a wide array of health issues, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Who Is at Risk?
Individuals with allergies, asthma, or compromised immune systems are at a higher risk for mold poisoning.
The risk also increases with prolonged exposure in damp environments such as basements, bathrooms, or places with water damage.
Contagion Concerns with Mold Exposure

Defining Contagion in Medical Terms
In medical terms, contagion refers to the transmission of a disease from one individual to another, typically through direct contact or airborne pathogens like viruses or bacteria.
Can Mold Spores Be Transmitted Person to Person?
Mold spores themselves are not contagious and cannot be passed from one person to another.
They are environmental contaminants that must be inhaled or ingested to cause health issues.
Mold Spores Versus Disease Transmission
Unlike infectious diseases caused by viruses or bacteria, mold-related health problems stem from environmental exposure and are not spread through interpersonal interactions.
Mold spores are ubiquitous in the environment and can start growing in suitable conditions, posing a risk to anyone exposed to that environment.
Environmental Spread Impacting Multiple People
If mold grows in a shared environment like a school or office, multiple individuals can experience symptoms due to the shared exposure, but the condition itself is not passed between them. It is the shared environment that is the common denominator.
Preventing and Addressing Mold-Related Health Issues

Mold Prevention Practices
Maintaining low humidity levels, ensuring proper ventilation, and promptly repairing any water leaks are key strategies to prevent mold growth in homes and workplaces. Regular cleaning and using mold-resistant building materials can also help.
What to Do If You Suspect Exposure?
If you suspect you’ve been exposed to mold, it’s important to identify and eliminate the source. Seek medical attention if you experience symptoms, especially if you belong to a high-risk group.
Treatment for Mold Exposure
Medical professionals may recommend antihistamines, nasal sprays, or decongestants to alleviate allergic reactions. In more severe cases, professional medical treatment might be necessary.
When to Call the Professionals?
When mold infestation is significant, professional remediation becomes necessary. Experts can safely remove mold and prevent its return, ensuring a healthy living or working environment.
Maintaining a Mold-Free Environment
Regular inspections, using dehumidifiers, and promoting good air circulation are effective in keeping an environment mold-free. Educating others about the risks of mold can also help protect public health.
FAQs About Mold Poisoning Contagiousness
Can mold poisoning be spread from person to person?
No, mold poisoning is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Is it safe to be around someone with mold poisoning?
Yes, it is safe to be around someone with mold poisoning as it is caused by exposure to mold toxins, not through human contact.
Does mold poisoning require isolation of the affected individual?
No, isolation of an individual with mold poisoning is not necessary since the condition is not infectious.
What causes mold poisoning if it is not contagious?
Mold poisoning, or mycotoxicosis, is caused by exposure to toxins produced by certain types of mold, not by contact with an infected person.
How can someone prevent mold poisoning if it’s not transmitted between people?
Preventing mold poisoning involves controlling moisture levels in your environment, promptly addressing water leaks, and removing visible mold growth with appropriate cleaning methods.
Final Thoughts
Mold poisoning, or mycotoxicosis, is a condition caused by exposure to mold toxins and is not transmitted between individuals.
It is important to understand that susceptibility and reactions to mold vary from person to person and are influenced by the specific circumstances of exposure, such as its duration and intensity.
