Yes, mold can make you itchy. Exposure to mold spores often causes allergic reactions, including itchiness. This reaction is due to mold’s irritants affecting sensitive skin. Consult a doctor if mold exposure leads to persistent itchiness.
Understanding Mold and Its Effects on Health

What Exactly is Mold?
Mold is a type of fungus that can grow both indoors and outdoors. It thrives in warm, damp, and humid conditions and reproduces by releasing tiny, lightweight spores that travel through the air.
These spores are present in almost all environments, and when they land on suitable surfaces, they begin to grow and form new mold colonies.
Common Indoor Molds
Several types of mold are commonly found in indoor environments. Aspergillus, Penicillium, Cladosporium, and Stachybotrys, also known as black mold, are among the most frequent culprits in homes.
Each type has its preferred conditions and can vary in color and appearance, but they all may pose risks to health.
How Mold Flourishes and Propagates?
Mold grows by digesting the material it is living on, which could be your walls, ceilings, or any organic material.
It spreads as spores are carried by air currents, insects, or even on clothing and shoes. Once a spore lands on a hospitable spot, it will start to sprout and spread if the conditions are right, with moisture being a key factor.
Health Issues from Mold
Exposure to mold can cause a variety of health problems. Some people may experience mild symptoms like a stuffy nose, sore throat, coughing or wheezing, burning eyes, or skin rash.
Others may have more severe reactions, especially those with mold allergies or compromised immune systems.
Allergic Reactions to Mold Spores
When sensitive individuals inhale mold spores, their immune system can overreact, leading to an allergic reaction.
Symptoms can include sneezing, runny or blocked nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes. In some cases, mold exposure can trigger asthma attacks in people with asthma.
Connection Between Mold Exposure and Itchiness
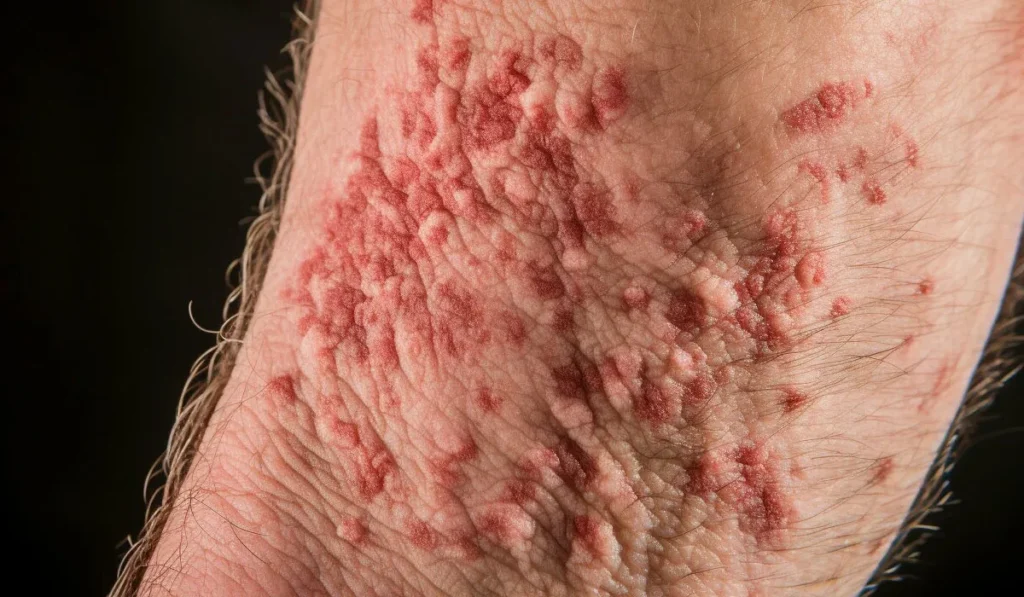
The Allergic Response to Mold
Mold spores can cause an allergic reaction that leads to itchiness.
This happens because the body’s immune system recognizes the spores as foreign invaders and releases histamine, a compound that causes inflammation and itchiness, in an attempt to defend the body.
Mold as an Irritant
Beyond allergies, mold can also irritate the skin and respiratory system directly. Touching mold or being in an environment with a high concentration of mold spores can lead to itching, redness, and skin discomfort.
Symptoms of Mold Exposure
Signs of mold exposure can vary from person to person but often include symptoms like skin irritation, itchiness, redness, and sometimes rashes.
Respiratory symptoms are also common and can include coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Severe Reactions and Mycotoxins
In severe cases, some molds produce toxic substances called mycotoxins that can lead to more serious health problems.
Mycotoxins can cause symptoms such as persistent headaches, fatigue, and even neurological issues in extreme cases.
Immediate vs. Delayed Reactions
Reactions to mold can be immediate or delayed. Immediate reactions happen within minutes to hours, while delayed responses may take days to appear.
This can make it difficult to identify mold as the cause of itchiness since the reaction is not always instantaneous.
Prevention and Treatment of Mold-Related Itchiness
Reducing Mold Growth
To prevent mold growth, it’s important to control moisture levels in your home.
Use dehumidifiers and air conditioners to reduce humidity, fix leaks promptly, and ensure proper ventilation, especially in areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and basements where moisture is common.
Mold Removal Techniques
If mold is already present, it needs to be removed carefully to avoid spreading spores.
Small areas can often be cleaned with soap and water or a mold-killing solution, but larger infestations may require professional mold remediation services.
Treating Skin Irritation from Mold
If you’re experiencing skin irritation due to mold, over-the-counter antihistamines and creams may help alleviate itching.
Keeping the skin clean and avoiding further contact with mold will also aid in recovery.
Seeking Medical Advice
If mold exposure leads to persistent itchiness or other severe symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor.
Health professionals can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, which may include prescription medications for allergies or skin conditions.
Long-Term Allergy Management
For individuals with mold allergies, long-term management may involve regular cleaning to keep mold at bay, using air purifiers with HEPA filters to capture spores, and possibly immunotherapy.
It’s also wise to avoid areas that are likely to have high mold concentrations, such as compost piles or fallen leaves.
FAQs About Mold and Itchiness
Can exposure to mold cause skin itchiness?
Yes, exposure to mold spores can cause skin itchiness as it often triggers allergic reactions.
Is itchiness a common symptom of mold allergies?
Yes, itchiness is a common symptom among individuals who have allergies to mold.
Why does mold exposure lead to itchy skin?
Mold exposure leads to itchy skin because mold contains irritants that can affect sensitive skin.
What should I do if I experience persistent itchiness after mold exposure?
If you experience persistent itchiness after mold exposure, you should consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Are there other allergic reactions to mold besides itchiness?
Yes, other allergic reactions to mold can include sneezing, coughing, runny nose, and watery eyes.
Final Thoughts
Mold exposure can indeed cause itchiness as it triggers allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
The irritants in mold affect the skin, leading to uncomfortable itching sensations. If you’re experiencing persistent itchiness due to mold, it’s advisable to seek medical advice to manage your symptoms effectively.
