Mold can be dangerous, particularly to individuals with allergies, asthma, or compromised immune systems. It produces allergens and irritants, and in some cases, toxic substances called mycotoxins. Prolonged exposure can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems.
Understanding Mold and Its Various Types
What Is Mold?
Mold is a type of fungus that can grow indoors and outdoors. It thrives in damp environments and reproduces by releasing tiny spores into the air.
These spores can land on surfaces and, if conditions are right, start to grow into new mold colonies. Mold can come in many colors, like black, white, green, or even pink.
Common Household Molds
Several types of mold commonly appear in homes and buildings. Aspergillus is often found on food and in air conditioning systems.
Cladosporium usually grows on fabrics and wood surfaces. Penicillium can spread on insulation, furnishings, and water-damaged furniture.
Stachybotrys, also known as black mold, is notorious for its dark color and potential health risks.
It tends to grow on materials with high cellulose content, like drywall, when they become water-damaged.
Conditions Favoring Mold Growth
Mold loves moisture. High humidity, leaks, or flooding can create the perfect home for mold.
Warm temperatures also encourage mold growth, as does any organic material like wood, paper, or dirt.
When mold finds such a spot, it can grow quickly and start to spread throughout a home.
Where Mold Hides?
Mold can grow in many places. Bathrooms and kitchens are common because they have a lot of moisture.
Basements, attics, and HVAC systems are also typical spots for mold because they can be damp and are not always well-ventilated.
Sometimes, mold grows in places we cannot easily see, like inside walls or under carpets.
Recognizing Mold Presence
It is important to know that mold can be both visible and hidden. You might see it as a fuzzy growth on surfaces or notice a musty smell.
If you suspect mold is growing out of sight, it might be time to have a closer look or call a professional for an inspection.
Health Risks Associated with Mold Exposure

Understanding the Health Impacts
Mold can affect your health. For some people, it causes allergies like sneezing, runny nose, or red eyes.
Others might experience asthma attacks or have trouble breathing. Even if you are not allergic, mold can irritate your skin, eyes, nose, throat, and lungs.
The Perils of Black Mold
Black mold, or Stachybotrys chartarum, is especially concerning because it produces toxic chemicals called mycotoxins.
These can lead to serious health problems if people are exposed to them over a long time. It is essential to get rid of black mold quickly and carefully.
Who Is at Risk?
Some people are more vulnerable to mold than others.
Babies and children, older adults, and those with weak immune systems or chronic lung diseases may get sick more easily from mold. They need to live in places with good air quality and without mold.
Connection to Serious Health Issues
Mold can cause infections in people with weakened immune systems. There is also research looking into whether mold exposure is linked to other health problems.
It is crucial to keep your home mold-free to protect your health.
Prevention and Remediation of Mold
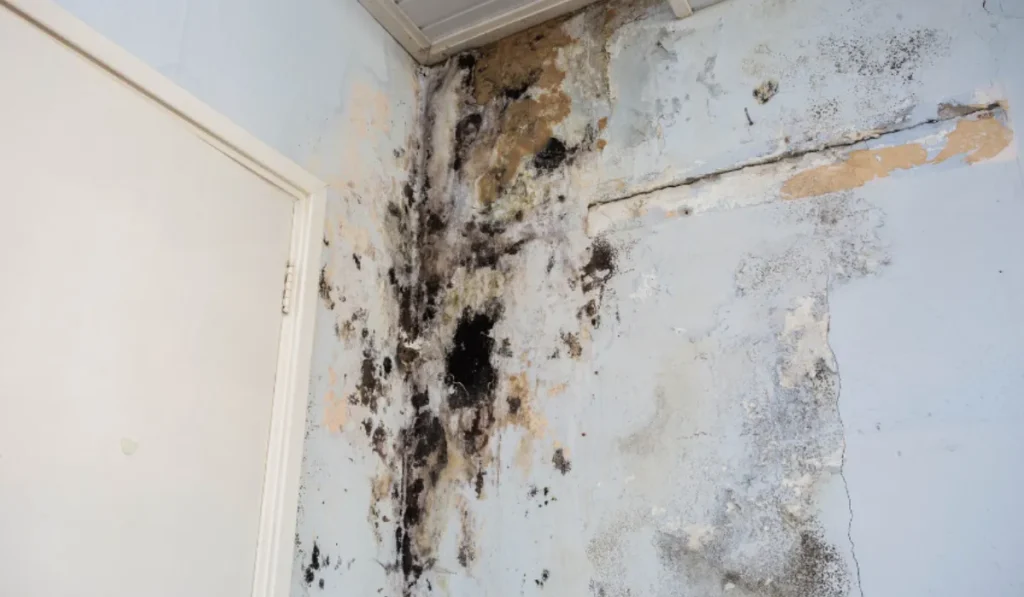

Keeping Mold at Bay
Preventing mold growth is key. Keep humidity low, fix leaks fast, and make sure your home is well-ventilated.
When building or remodeling, choose materials that resist mold. These steps can help stop mold before it starts.
Identifying Mold in Your Home
Look for signs of mold regularly. Check for spots on walls or ceilings, a musty smell, or health symptoms like allergies that could suggest mold is growing in your home.
Taking action early can prevent bigger problems later.
When to Call the Experts?
If you find mold or suspect it is hidden, you may need a professional to assess the situation. They can test for mold and help you understand the extent of the problem.
Knowing when to get help is important for your health and your home’s safety.
Removing Mold Safely
Small mold problems might be something you can handle. But for larger issues, or if black mold is involved, it is best to have professionals do the work.
They have the right tools and know-how to remove mold safely and effectively.
After Mold Cleanup
Once the mold is gone, keep an eye out to make sure it does not come back. Use dehumidifiers, fix any leaks right away, and clean regularly.
Have your home inspected from time to time to ensure that it stays mold-free.
FAQs About the Dangers of Mold
How harmful is mold to individuals with allergies or asthma?
Mold can be particularly harmful to individuals with allergies or asthma, as it produces allergens and irritants that can trigger symptoms and exacerbate these conditions.
Can mold exposure affect the immune system?
Yes, mold can be dangerous to people with compromised immune systems, potentially leading to more severe health issues.
What are mycotoxins, and how do they relate to mold?
Mycotoxins are toxic substances produced by certain types of mold, and they can pose serious health risks if ingested or inhaled.
What kind of health problems can result from prolonged mold exposure?
Prolonged exposure to mold can lead to respiratory issues, allergic reactions, and other health problems, especially in sensitive individuals.
Is short-term mold exposure also dangerous?
Short-term mold exposure can irritate the eyes, skin, nose, throat, and lungs, even in people who are not allergic to it.
Final Thoughts
Mold poses significant health risks, especially for those with allergies, asthma, or weakened immune systems.
It generates allergens, irritants, and potentially mycotoxins, which can be toxic. Chronic mold exposure may lead to serious respiratory issues and other adverse health effects.
