Yes, Aspergillus is a type of mold. It’s a genus of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus commonly grows on decaying vegetation and is also prevalent in indoor environments.
Aspergillus Definition and Classification

What Exactly is Aspergillus?
Aspergillus represents a group of molds, or fungi, that are found in various environments worldwide.
These organisms are microscopic, with a structure consisting of long, branching filaments known as hyphae that form a mycelium or network.
The Taxonomy of Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus within the Kingdom Fungi, classified under the phylum Ascomycota.
This classification is based on the presence of asci, a type of spore-producing cell. It is part of the order Eurotiales and family Aspergillaceae.
Differentiating Aspergillus from Other Molds
Aspergillus can be distinguished from other molds by its characteristic conidial head structure, which is used for asexual reproduction.
Unlike some other fungi, Aspergillus spores are typically asexual, known as conidia, and are produced in large quantities.
Common Species and Their Habitats
Several hundred species of Aspergillus exist, with some of the most common being Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus niger, and Aspergillus flavus.
These species are versatile and can inhabit a range of environments, often found in soil, decaying vegetation, and indoor air.
The Role of Aspergillus in Nature and Industry
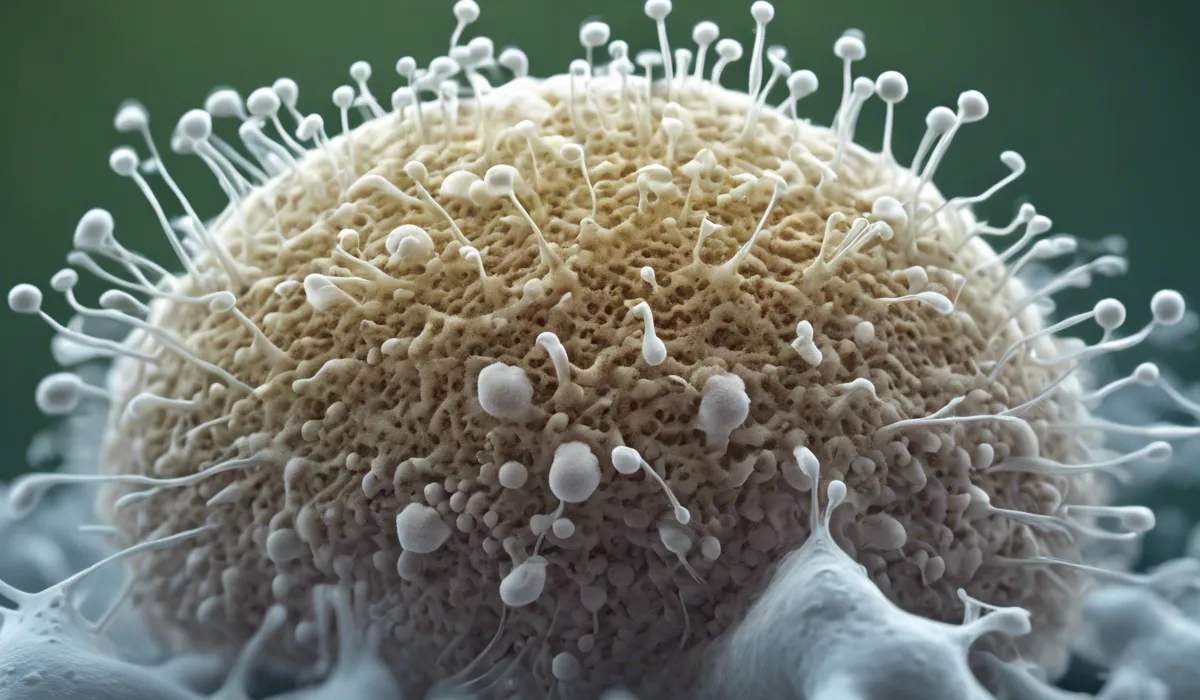
Aspergillus in the Ecosystem
Aspergillus plays a crucial role in the natural ecosystem. It contributes to the decomposition of organic matter, breaking down complex compounds into simpler ones that plants can use as nutrients.
Nutrient Cycling and Decomposition
Through decomposition, Aspergillus helps in the cycling of nutrients in soil ecosystems. It decomposes a variety of organic materials including dead leaves, wood, and other plant matter, thus facilitating nutrient recycling.
Applications in Food Production
Aspergillus is used in the production of many types of food. It is instrumental in the fermentation process for making soy sauce and miso, and certain species play a part in the maturation of cheeses.
Industrial Uses of Aspergillus
Industrially, Aspergillus is used to produce enzymes and organic acids like citric acid, which is integral to the food and beverage industry. Its enzymes are also used in detergents, textile processing, and paper pulp production.
Biofuel Production Potential
Research is ongoing into the use of Aspergillus in biofuel production. Its ability to break down plant cellulose could be harnessed to produce ethanol, providing a renewable energy source.
Health Implications of Aspergillus Exposure

Indoor Mold: Aspergillus Concerns
Aspergillus is commonly found indoors, growing on damp walls, in HVAC systems, and on organic matter like houseplants. It thrives in moist environments and can become a health concern if not properly managed.
Health Risks from Aspergillus
Exposure to Aspergillus can lead to various health problems. While most people breathe in Aspergillus spores without getting sick, those with weakened immune systems or lung diseases can develop serious infections.
Allergies and Aspergillus Infections
Allergic reactions to Aspergillus can range from mild to severe and include symptoms like asthma. Infections such as aspergillosis can be more severe, sometimes leading to chronic lung issues and other health complications.
Who is at Risk?
Individuals with compromised immune systems, those with chronic lung diseases or those taking medications that suppress the immune system are at a higher risk for Aspergillus-related health issues.
Detecting and Preventing Aspergillus
Detection of Aspergillus involves air quality tests and surface sampling. Prevention includes controlling humidity levels, fixing leaks promptly, and ensuring adequate ventilation in homes and workplaces.
Treating Aspergillus Infections
Treatment for Aspergillus infections can involve antifungal medications. Management of the environment to prevent the growth of Aspergillus is also crucial in treatment and prevention.
FAQs About Aspergillus
What exactly is Aspergillus?
Aspergillus is a genus of mold that includes several hundred species, commonly found on decaying vegetation and in indoor environments.
Can Aspergillus be found indoors?
Yes, Aspergillus is prevalent in indoor environments, often growing in damp or decaying organic material.
Is Aspergillus dangerous?
Some species of Aspergillus can be harmful, especially to individuals with weakened immune systems, causing allergic reactions or infections.
Where does Aspergillus commonly grow?
Aspergillus typically grows on decaying vegetation, such as compost piles, and can also thrive in areas of high humidity or dampness indoors.
How can I prevent Aspergillus growth in my home?
To prevent Aspergillus growth, control moisture levels, fix leaks, and ensure good ventilation to reduce dampness and humidity.
Final Thoughts
Aspergillus represents a genus encompassing several hundred species of mold. These molds are ubiquitous, thriving in a variety of climates globally and frequently found on decomposing plant matter.
They are also a common presence in indoor spaces, potentially affecting air quality and posing health risks.
